Balance training
BALANCE | EVALUATE • TRAIN • DOCUMENT
EVERYTHING EASY WITH BODITRAK2

Minimise risk & maximise quality of life
The BodiTrak2 Pro Pressure Measurement System is used by rehab professionals around the world to assess and document the pressure management, postural and comfort needs of their patients. Based on objective data, they develop individual seating and positioning solutions.
BodiTrak-Balance | Sensor
FLEXIBLE • MOBILE • ADAPTABLE
BodiTrak Balance Sensor Mats are flexible and mobile and can be used on a variety of surfaces, e.g. flat on the floor, on a step, over a balance board, air cushion, foam, and more. This enables a differentiated balance analysis for different situations and levels of difficulty.
Use with balance boards, foams or air cushions
The most popular sensors are 2’x 3′ and 2’x 2′
Recent studies
MAPPING BALANCE PRESSURE
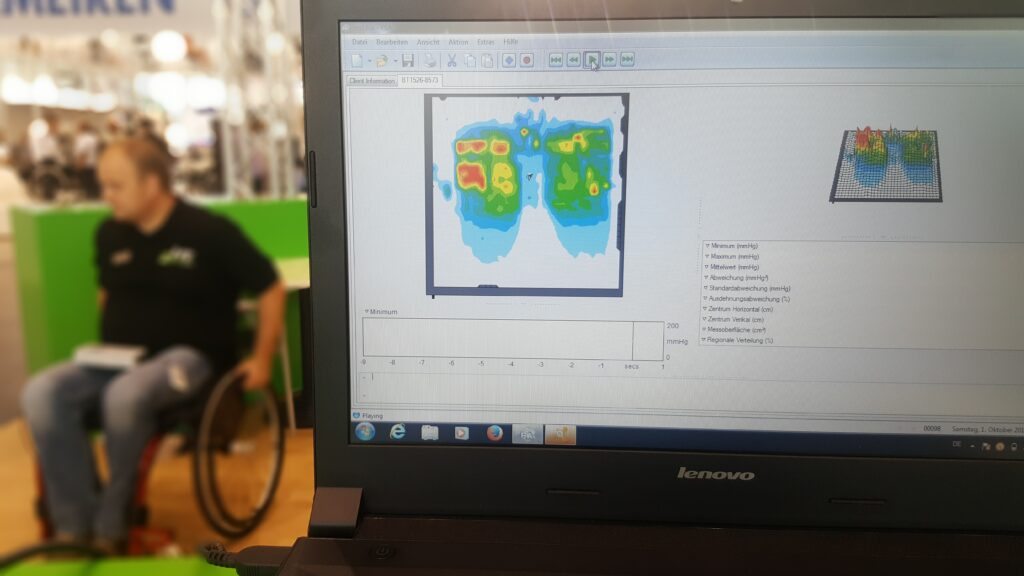
The BodiTrak Balance software uses a pressure measurement sensor to provide information about the centre of pressure and vertical forces on a video showing the patient’s movement and foot pressure. This data provides information on standing stability, range of motion, acceleration, standard deviation and weight bearing from side to side and heel to toe.
The centre of the pressure trace is easy to follow and is a powerful training tool that gives a quick, clear overview of how the patient is performing the assigned task. Statistical data and graphs in the reports document the therapist’s observations and optimise the continuation of therapy.
Click here for more information about Balance.
APPLICATIONS
Technical Data
| Specification | Balance mat small | Balance mat medium | Balance mat large |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | BT-1616-502 | BT-1625-510 | BT-1632-510 |
| Sensor type | Pressure | Pressure | Pressure |
| Sensor size | 25,4mm | 25,4mm | 25,4mm |
| Number of sensors | 256 (16 x 16) | 400 (16 x 25) | 512 (16 x 32) |
| Measuring range Length | 470mm | 730mm | 940mm |
| Measuring range width | 470mm | 470mm | 470mm |
| Calibration range | 20 & 40psi | 20 & 40psi | 20 & 40psi |
| Specification | Balance mat small | Balance mat medium | Balance mat large |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upper material | Black polyester & yoga mat | Black polyester & mat cover | Black polyester & mat cover |
| Bottom material | Black polyester & yoga mat | Black polyester & running mat | Black polyester & running mat |
| Connection and power supply | USB-A | USB-A | USB-A |
| Cable length | 91cm | 30cm | 30cm |
| Total length | 610mm | 914mm | 1143mm |
| Total width | 610mm | 610mm | 610mm |
| Scan Rate | 100Hz | 100Hz | 100Hz |
*About the MCTSIB
The MCTSIB evaluates balance performance, specifically how sensory inputs are used when one, two or all sensory systems are removed.
In condition 1, all sensory systems are available and the patient should have no difficulty maintaining balance (with feet shoulder-width apart and arms crossed over the chest) on the solid surface for 30 seconds with eyes open.
In condition 2, the vision sensor system is removed (as the patient is asked to keep their eyes closed) while maintaining their position for 30 seconds. The patient can rely on the other two systems to maintain balance.
In condition 3, the somatosensory system is removed (patient stands on foam, unstable surface). The patient can rely on vision and vestibular inputs for balance.
In state 4, both the somatosensory and visual systems are removed (patient stands on foam surface with eyes closed). The patient can only rely on inputs from the vestibular system for balance.
Failure to maintain balance:
–> Failure in state 2 indicates that the patient relies on visual input to maintain balance;
–> Failure in states 3 & 4 indicates that the patient relies on somatosensory input to maintain balance and that the visual and/or vestibular systems are not being used and are likely to be impaired.
** The modified CTSIB is a simple to administer test that assesses the patient’s ability to stand upright under a variety of sensory conditions It was shortened from the original CTSIB in condition 6 following a study by Cohen et al on three groups of neurologically asymptomatic adults (young, middle-aged and elderly) and a fourth group of subjects with vestibular disorders.





